User testing is the most crucial step of UX design since it helps to determine whether users will be satisfied with a product and whether their expectations will be met. User research is essential in gathering user feedback and insights, which can significantly improve product design.
Since getting information from the targeted audience is possible, designers can avoid potential interfaces and enjoyment problems while building up the concepts, making the users’ interaction with the product more pleasant.
In this article, we will describe how to conduct user testing and suggest twin approaches for gathering user feedback to improve the design. It includes everything from the effective structuring of test sessions to the interpretation of the results and subsequent changes in the design, and it will help to raise user testing for UX design improvement.
What Is User Testing?
User testing, or usability testing, is a critical research method involving the users in examining a product or service. Such a scheme entails creating a sample of users representative of the target users and conducting the sessions in a simulated environment to monitor their actions and responses.
The primary objective of user testing is to obtain both qualitative and quantitative data that explain the efficiency of the design to the user requirements.
Usability testing focuses on evaluating how effectively users can interact with a product to achieve designated objectives, emphasizing design intuitiveness and direct input from real users. This data can be user comments, percentage of tasks completed, counted errors, and time taken to finish particular tasks.
Source: getuplift
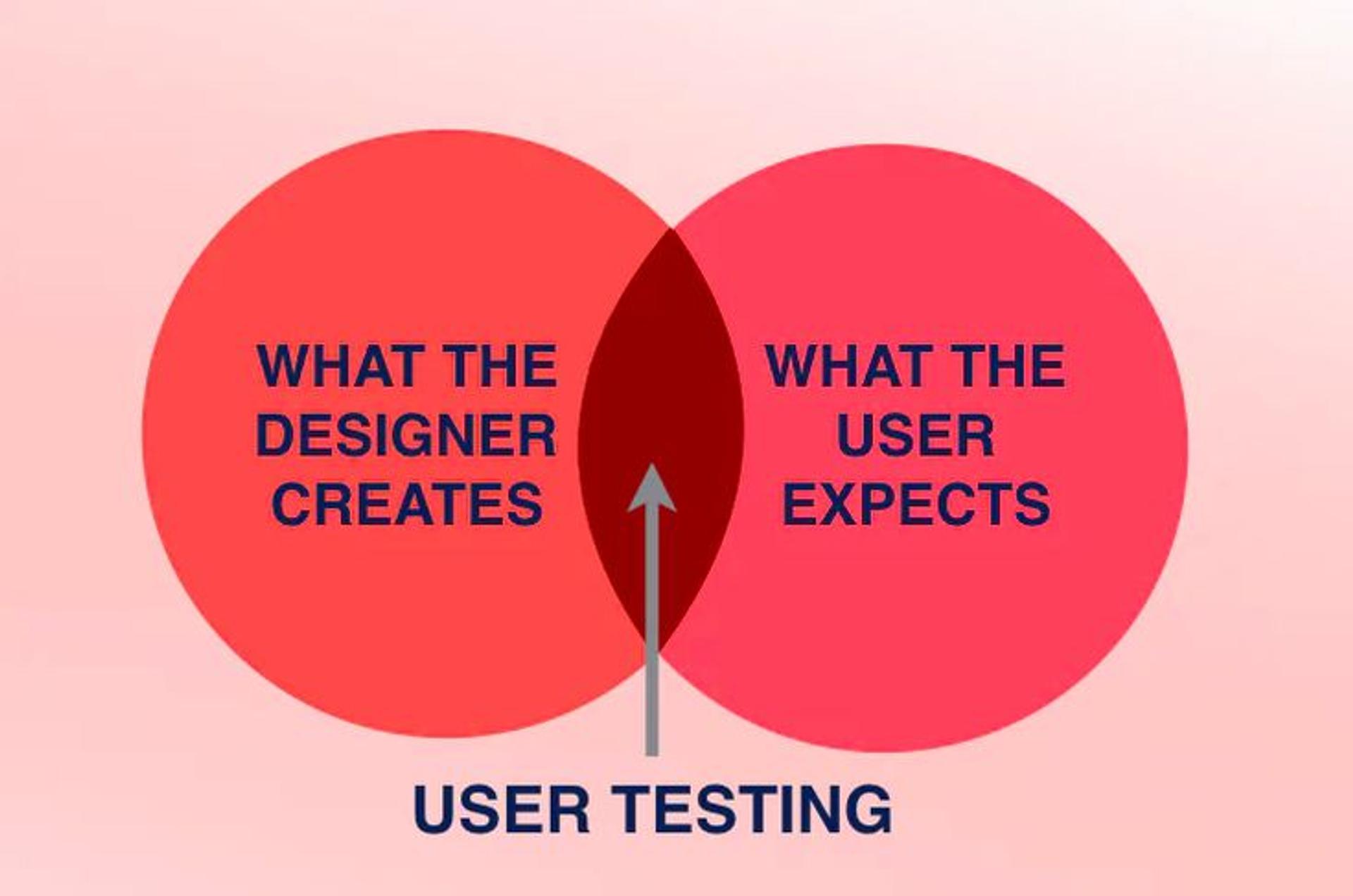
Usually, more than a couple of user testing iterations are spread out across the design process, helping designers prevent usability problems like annoying or irrelevant paths or buttons on the interface.
In addition, user testing provides the ability to measure user satisfaction and identify problems that need to be resolved to improve the functionality and usability of the interfaces.
Designers have essential information that will be useful in making changes to the product by watching users use the product to perform tasks, navigate, and voice their opinions. These insights help make the final and ultimate product, aimed at the specific audience, much more built with less frustration in its use.
Why Is User Testing Valuable?
User testing is beneficial as it links designers directly with the most essential part of the project: the end users. By conducting a user test to evaluate a product's usability through various testing methods, designers usually get information that needs to be included in surveys and other more traditional techniques.
This primary evaluation helps note issues that users could report more easily regarding general usability and performance comparison with their expectations.
In addition, there is an emphasis on user testing because such activities encourage looking at everything from the user’s point of view rather than making decisions based on mere assumptions about the users.
Source: nngroup

User testing is constructive and adopted at every design process step. While working in this mode and collecting feedback, bases can produce improvements for users and help users achieve their goals.
Ultimately, these uplift the product in terms of usability and ease of use and increase satisfaction and retention, which are essential for any digital solution.
This approach to UX practice enables management organizations to develop high-quality products and mitigate the risks of launching those guarantors do not want to harness, which is a critical feature of great UX design.
Planning Your User Testing
To conduct fruitful user testing, the first step that must be taken is to recruit test subjects, which provides the support required for comprehending the needs of the tested subjects and ensuring that the procedure in question is streamlined and effective.
In the below paragraphs are some of the crucial aspects that need to be taken into consideration while planning your user testing sessions:
Setting Clear Objectives
Identifying user testing goals is a critical asset for the productivity of the entire exercise. Emphasize some of the queries you would like answered, such as whether users can easily access and ease certain features with which they are likely to behave in a given situation or are satisfied with the product.
Source: examples

The objectives, which aim at the specific core aspects, not only help weave the sessions but also act as the gauge to check what success has brought.
Once you have these goals, the decision becomes more accessible as resources will be directed appropriately, and the design meeting the data needs will be developed using the appropriate testing method.
Identifying Your Target Audience
Feedback can only be considered valid when obtained from test subjects selected to represent the target audience. Consider age, gender, level of expertise, and other important factors related to the solution being worked on.
This variation in sample types increases the scope of the collected feedback as it cuts across all the users, thus enhancing the design and development of the product. Sampling a subgroup of users in this manner is also helpful in finding problems of usability and information that they would not otherwise be able to come across.
Source: Akwatoria

Choosing the Right Testing Methods
Since a range of testing approaches are available to the tester, selecting the test method that meets the study’s aims and provides the maximum utility is wise. This includes tests that employ moderators at various stages or do not perform them remotely or in person, as well as qualitative and quantitative testing.
Moderated usability testing involves direct interaction between a researcher and users, allowing for real-time feedback during product interaction. This method is particularly useful for identifying usability issues and understanding user preferences.
The advantages of each method can be extended and will all depend on what specific information you will be targeting. For example, moderated testing is appropriate for capturing user mental models, while unmoderated can be more efficient and more prominent in size.
With careful consideration of various methods, you are placed on the right path of achieving the right balance between insight depth and breadth.
Focusing on these crucial elements while planning helps you enable a more insightful user testing process. Such intensive preparatory work results in a product that is likely to be well received by users, thus helping meet their requirements and achieving a higher level of satisfaction. Careful planning of user testing can greatly help enhance the overall quality of the product.
Source: dribbble
Elements of Usability Testing
Usability testing is a vital aspect of the user experience (UX) design process, focusing on evaluating a product by testing it with real users. This practice aims to identify usability problems, assess user satisfaction, and understand how easily users interact with a product.
Facilitator
A facilitator is a vital person present in usability tests who oversees that participants complete all activities during testing while ensuring the application of neutrality in the process.
An efficient facilitator has done their homework, has a plan, and is flexible enough to understand the situation as it develops to make it easy for the participants. Such skill is central to eliciting maximum response or giving the respondents their views.
Source: luis-goncalves

Environment
The location and surroundings of the participants during the tasks play an important role in efficiency and comfort. The environment should be devoid of irrelevant elements and replicate the real-world scenarios in which the product will be used.
Think about the location, such as in what circle lights, headphones, or telephones are helpful for interaction with others and will foster the experience rather than using fake circumstances.
Documentation
Comprehensive documentation during usability testing is essential for tracking observations, participant feedback, and any issues encountered. This documentation is a reference point for analysis and fosters a clearer understanding of user interactions and experiences over time.
Thus, teams will be able to improve the usability performance of usability tests, making it possible to create products that their users will enjoy.
Feedback Mechanism
The process of gaining feedback can be accompanied by some aspects that allow the participants to offer their opinions about the testing process. This may be in the form of their impression about the outcomes of usability testing and what was being asked, including any other information that might help the researchers improve the usability test, such as whether the process was easy or difficult.
Source: atlassian

How Does User Testing Work?
User testing is a systematic approach to testing a product by watching real users perform various activities with the product. This process usually starts with establishing the test’s objectives and goals, which helps to define the areas of focus, be it usability, functionality, or user preferences with designs, while considering the testing environment to avoid disruptions due to technical issues.
The next step is to consider the selection of a sample of users, who corresponds to the group of people for whom the product is designed. This assures that the information derived from the tests would be of great value.
When the participants have been enlisted, an organized strategy is drawn containing the activities each user will perform or is likely to perform in the encounter. These activities are intended to reproduce actual situations to obtain realistic responses. The users are administered ‘thinking aloud’ methods during the testing process.
Source: flowmapp

They are asked to say anything that crosses their mind, including negative emotions towards the product being tested by them. The tasks performed concerning the study include sketching notes and capturing videos of the users undertaking activities to obtain qualitative and quantitative information for analysis.
Once the test sessions are over, the data captured is analyzed and synthesized to highlight issues that may be area challenges or even pain points.
This analysis is essential as it helps make any necessary changes to the product’s design, as the users take into account. Ultimately, user testing is an efficient tool that enhances design along the user-oriented line by improving products to users’ satisfaction.
Conducting Effective User Tests
Practical user tests are essential to gather meaningful insights that drive product improvement. Here are the key points to focus on:
- Creating Realistic Scenarios: It is vital to design test scenarios that closely mimic real-world usage. This helps users feel comfortable and reduces the likelihood of atypical behavior during the test, leading to more authentic feedback.
- Selecting Appropriate Tasks: Choose tasks that reflect the product’s most critical functionalities. These tasks should be relevant to the user goals and represent typical interactions, enabling testers to evaluate the product effectively.
- Recruiting the Right Participants: Selecting participants resembling the target user demographic is crucial for obtaining relevant insights. Engaging user testing services can help recruit suitable test subjects for large-scale projects, streamlining the process and ensuring a diverse group of testers captures a wide range of user experiences and perspectives.
- Moderating Sessions Effectively: A skilled moderator can elicit valuable feedback by encouraging users to express their thoughts and feelings while navigating the product. The moderator should balance guidance and observation, allowing users to explore naturally while ensuring the test remains focused.
By emphasizing these core aspects, designers can facilitate practical user tests that yield valuable insights for enhancing usability and overall user experience.
Analyzing and Interpreting Results
The analysis and evaluation of the results of a usability test represent the last step, the most important one since it evaluates data collected to provide helpful information. Key aspects include the following:
Qualitative Data vs. Quantitative Data
In this case, clearly distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative data is essential. Qualitative data, mainly user comments and observations, gives an in-depth understanding of the controllers' actions and driving forces. On the other hand, metrics and statistical analysis form part of quantitative data and help illustrate the problems of usability and user satisfaction.
Source: Akwatoria

Identifying Patterns and Trends
After collecting data, the next step involves diagnosing some of them as logical and recurrent themes or patterns. This requires that qualitative comments be coded and quantitative questionnaire data be used to identify problem areas, likes, and successful elements. These trends may offer more in-depth reasoning as to why users do certain things and assist in building structure.
Prioritizing Issues and Opportunities
None are equally important; therefore, the number one goal should be to surface the findings that affect user experience. The designers need to determine which user issues are the most recurrent and which are the most critical to user operations. By doing whatever was prioritized first, the teams will improve the degree of usability and satisfaction of the product concept's users.
To conclude, analyzing and interpreting user testing outcomes are critical in improving designs that meet users' needs and enhance the product's usability.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Website usability is crucial, but several common pitfalls can hinder its effectiveness. Awareness of these challenges and avoiding them can help ensure more accurate and actionable insights.
Leading Questions
One of the most significant issues in user testing is using leading questions that can bias the participant's responses. To avoid this, moderators should frame questions neutrally and avoid suggesting preferred answers. Open-ended questions encourage participants to share their genuine thoughts without influence.
Source: userpilot

Confirmation Bias
Testers may unconsciously seek data that confirms their pre-existing beliefs about the product, which can skew results. To combat confirmation bias, ensure that a diverse team is involved in the analysis phase, encouraging multiple perspectives to review findings objectively and consider contradictory evidence.
Over-Testing
Conducting too many tests can lead to fatigue among participants, diminishing the quality of feedback. It's crucial to strike a balance by planning test sessions efficiently, focusing on critical areas of the product. Additionally, limiting the number of variations being tested at any time can help maintain participant engagement and ensure more precise insights.
By being mindful of these pitfalls, teams can conduct more effective user tests that garner genuine user insights, ultimately leading to better design outcomes.
Read more:
Conclusion
In conclusion, usability testing is integral to every designer's work since it helps them understand the user's experience with a product and its user interface. Efficient ways of performance, including using real-life situations, assigning suitable objectives, and choosing the appropriate respondents, enable the teams to obtain valuable information that should enhance the designs.
In addition, an adequate evaluation of the outcomes makes it possible to extract insights that are helpful in order of importance for addressing the pain points that are most troublesome to users. Looking out for some familiar sources of error, such as leading questions and confirmation bias, is essential in reducing feedback errors.
Considering that user experience design is a process, other user testing will still be significant for product enhancement to meet changing user needs. Finally, a user feedback approach ensures a user-centered process is adapted for product development.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


