In today’s world, user experience (UX) design has become integral to product or service achievement. Human-computer interaction serves as a foundational element in UX design, informing the methodologies used in interaction design and usability testing.
It aims at improving user satisfaction through better usability, accessibility, and interaction between the user and the product. As technology changes and improves, people have come to understand the need to integrate UX design into their business strategies.
To further understand, this paper will focus on four key UX design disciplines that enhance user experience: user research, interaction design, information architecture, and visual design. All these are required to create and build alluring and practical interfaces for particular market users.
Source: zonicdesign.ch

Understanding User Needs
Comprehending user expectations is a fundamental step in the sequence of steps in UX design. This entails multidisciplinary approaches aimed at understanding users' behaviors, needs, and motivations to enhance design.
User research is essential in this procedure; it applies different methods like interviews, surveys, usability testing, and contextual inquiry to collect helpful information.
User research plays a big part in defining the user persona, journeys, and flows, which are crucial to user-centered design. Products that match each user's expectations can only be made through information about user requirements and needs.
One such example is a UX designer creating a mobile app who then has to ask users questions about issues related to them. The team uses this information to develop appropriate features for the app that users will find easy to use.
User Research
User research is one of the design disciplines that elucidates users' needs, behaviors, motivations, and issues. It helps inform a design that is relevant to those for whom it is being implemented.
User research entails different qualitative and quantitative strategies, such as interviews, surveys, usability testing, and field studies. These approaches help gather helpful information about audiences' preferences and use of companies' products.
Interviews and Surveys: Personal interviews and surveys help designers understand users' subjective ways and collect direct responses. This technique uncovers individual perceptions, sentiments, and experiences that could be valuable in optimizing designs.
Usability Testing: Testing a product with its end users helps to understand how they use it and what irritates them. This testing provides essential information such as kinetic behavior, where the user frequently meets obstacles, and the sequence taken through the site.
Field Studies: Collecting samples by persons who use the product occupied in its intended context gives high-quality information. It shows how people use the product daily and the obstacles they face.
Thanks to these research techniques, developers can create user-oriented designs that solve real user issues, increase user satisfaction with the product, and contribute to its success. Appropriate user research is helpful at each stage of the UX lifecycle and improves the chances of meeting users' needs even more.
Source: toptal

Additional resources
Books:
- "Observing the User Experience: A Practitioner's Guide to User Research" by Mike Kuniavsky: This book provides a comprehensive guide to the various methods of user research, with real-world examples and practical advice.
- "Just Enough Research" by Erika Hall: A concise and direct guide to conducting effective user research without data overwhelm.
Websites and Articles:
- Usability.gov - Managed by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, this site contains resources on user-centered design and research strategies.
Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture (IA) is one of the UX design disciplines that creates a structure for the content, enabling users to quickly search for the required content. This component of IA improves interaction with users by helping to avoid confusion in how data is presented. IA includes organizational systems, labeling, navigation, and searching abilities:
- Organization Systems: This outlines the mode of grouping and structuring the content to minimize problems in the flow of information.
- Labeling Systems: This comprises the various techniques employed to name the content and illustrate its respective categories for proper retrieval. Simple categorization no longer restricts users to document files and attachment locations.
- Navigation Systems are how users navigate the different content areas within the product interface and content layouts.
- Search Systems: Enhanced search functionalities are embedded within the interface, allowing users to search for specific details quickly and improving their height and satisfaction.
User interface design plays a crucial role in enhancing user interaction by balancing aesthetics with usability, ensuring that the product is not only visually appealing but also easy to navigate.
Source: medium
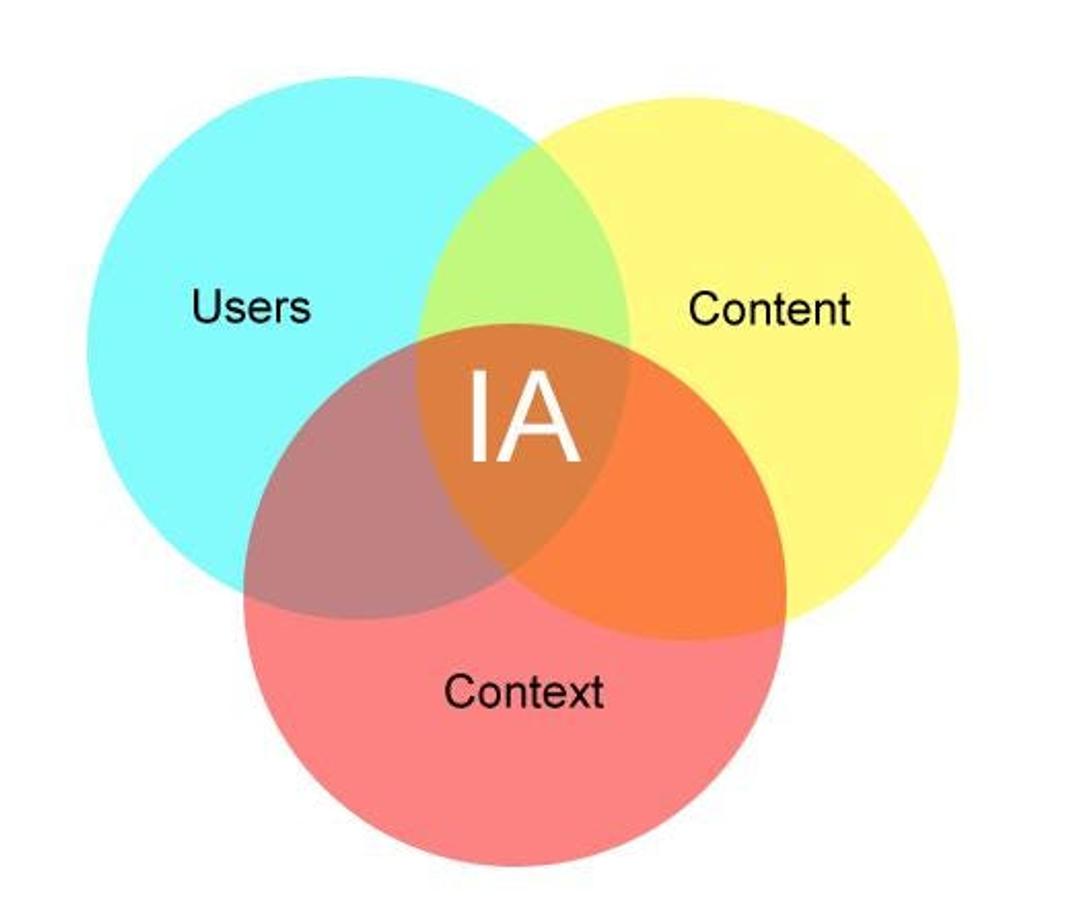
Emphasizing the constituents also helps to address the IA concerns, improving the overall efficiency of the product. For example, an e-commerce site with a built-in IA allows customers to search and browse for products and even make purchases with relative ease, enhancing the likelihood of their engagement and conversion.
Additional resources
Books:
- "Information Architecture: For the Web and Beyond" by Louis Rosenfeld, Peter Morville, and Jorge Arango
Websites:
Experience Strategy (ExS)
Experience Strategy (ExS) is a detailed and specific discipline of UX that describes how a business intends to create superior user experiences. This strategy seeks to bridge the gap between what the company wants to achieve and what its users want and expect to derive from the company and its products.
An experience strategy is more in-depth than simply understanding users, planning for users, and designing for them; it is understanding the users, anticipating their needs, and developing and implementing new solutions to satisfy them. The general components of ExS are:
- User insights: Conducting qualitative and quantitative research to identify and analyze users’ behaviors, goals, and challenges. This enables the design decisions to be supported by all relevant information and data and, therefore, be user-centered.
- Business Alignment: Achieving the business objectives utilizing user experience strategies, including growth, customer satisfaction, and retention.
- Cross-functional: Integrating efforts from different departments whose insight or involvement is required in ensuring a coordinated user experience.
- Continuous Improvement: User experience is constantly improved, adapted, and developed until users are no longer satisfied and adequate technology has been developed.
Concentrating on these components allows organizations to provide experiences that are not only as good as users expect but even better, cultivating users’ loyalty.
Source: medium
Additional resources
Books
- "This Is Service Design Doing" by Marc Stickdorn, Markus Edgar Hormess, Adam Lawrence, and Jakob Schneider
Websites
- Service Design Network: A platform offering articles, case studies, and insights into service design as a strategic experience enabler.
- UX Matters: A valuable resource for trends, techniques, and best practices in UX and experience strategy.
Interaction Design
Interaction design is a discipline of the UX design process that considers the design of appealing user interfaces that influence users' interactions with a product.
It concentrates mainly on user-product relations, that is, the actions that users perform and the actions aimed at users, in this case, to create a more pleasant, fluid, and intuitive encounter.
An interaction designer plays a crucial role in this process by identifying user goals and determining the necessary tools for efficient user interactions. Some of the key elements which inform principles of interaction design include:
- Consistency: Creating user flows that ensure the exact behavior of any group of similar elements eliminates frustration in the user experience. Consistency in the interface reduces clients’ degree of newness and increases productivity.
- Feedback: Given the online interactions where an individual may perform actions through clicks, it is essential to see a response from the system, be it sound or light, to reassure the individual that their action has been recorded. This affirmation eases the processes and does not break the loop of faith that the users have in the app that it will respond.
- Efficiency: Structuring interactions where, in most cases, the user succeeds in overcoming the objectives set only by investing minimal effort. Efficiency can be achieved through a system that quickly uses or commonly uses ideas with other anthropological strategies, lessening everything users must think about to accomplish a given task.
Source: medium

Through these practices, interaction design increases several key performance indicators among users, such as user engagement and satisfaction.
It guarantees that all users can complete tasks without breaking a sweat, thus enhancing their belief in the product and making the overall experience pleasurable.
Better design interventions in the interaction process translate to greater efficiency in the product's user retention rate and, hence, profitability.
Additional resources
Books:
- "Designing Interactions" by Bill Moggridge
- "About Face: The Essentials of Interaction Design" by Alan Cooper, Robert Reimann, and David Cronin
Websites:
Continuous Learning and Improvement
UX designers must keep learning new things and improving themselves. Considering that UX design will be developing fast, designers must embrace the changes in the profession.
This entails education and training, keeping up-to-date with the market, and wanting to be perfect by improving the design by considering the users and other interested parties.
Continuous learning and improvement become relevant, especially in product delivery. They enable the design purposes to be Original and, in addition to the design, enhance the product's usability. Communicating well with the users and stakeholders to get feedback was one way to improve the designs.
For instance, the UX designer can relate to other professionals by attending conferences, taking particular workshops, and encouraging the reading of new trends in the field.
This zeal for improvement allows them to incorporate the most relevant techniques in their practice, which translates into better-quality products.
Learning and enhancing staff skills are also necessary for career advancement. Searching for all relevant information and knowledge leads to growth for the designers and exposes them to new roadblocks that they could tackle.
Apart from these, constant learning and improvement show dedication to excellence and enthusiasm for designing products that satisfy the user's needs.
In summary, the user-centered principles comprising the user needs analysis, user research, and the focus on an ongoing improvement cycle are central to the UX design process.
With this knowledge and insights regarding user behaviors, needs, and motivation, the designers generate artistic products that fit the users' expectations for an appealing experience.
Learning from others in the field and developing the ability to seek out and manage improvements will allow the ending of neck top designing.
Read more:
Conclusion
Overall, four primary areas of concentration—content strategy, visual design, usability testing, and user-centered design—create excellent experiences.
Every area of focus has a unique function, and when integrated, they create a complete cycle of thinking around the agility of product development, from ideation to engagement.
Content strategy keeps the message accurate and focused, and the visual design appeals to the user and provides functional ease. Usability testing is essential as it assists in looking at things from the end users’ perspective while offering potential improvements through iteration.
This allows the organizations to develop products that users would be pleased with and earn product market fit and love. However, it is time to incorporate these elements into your design process to achieve a holistic balance between impact and usability.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


