Successful businesses grow around products, which is why product design is inevitable. It includes a whole series of activities, from conceptualization through development to the improvement of the products that address users’ needs while considering the goals of the business, the possibilities of technology, and insights from market research.
By merging the knowledge of users, the current market, and the scope of technology, product design increases tremendous and exciting client experiences.
In this section, we shall look into the fundamental aspects of product design and how it helps develop new and modern ways of problem-solving devices. It is time to reverse the talks of product design in this segment, which is more beautiful than the stroke explaining how product design makes great things happen.
What Is Product Design?
Product design is the process of identifying a market opportunity, clearly defining the problem, developing a proper solution for that problem, and validating the solution with real users.
The key principles of product design include desirability, feasibility, and viability. Desirability considers whether or not the product is wanted or needed by the target users.
Feasibility considers whether or not the product is achievable in terms of technology, materials, and resources available. Viability considers whether or not the product makes smart business sense.
Desirability is a critical aspect of product design, as it ensures that the product meets the needs and wants of the target users. Feasibility is also essential, as it ensures that the product is achievable and can be developed within the available resources. Viability is crucial, as it ensures that the product is profitable and contributes to the long-term growth of the business.
Source:miquido
By considering these key principles, product designers can create products that are desirable, feasible, and viable, ultimately leading to business success and user satisfaction. In the next section, we will explore the product design process and the steps involved in creating successful products.
Definition and Importance of Product Design
Product design is a process that involves understanding the business objectives and user experience of a product. It is a crucial aspect of product development, as it helps businesses and brands to achieve their goals and objectives. Product design is essential for creating products that meet user needs and are competitive in the market.
What Are the Steps of the Design Process?
Here are the steps of product design cycle:
1. Discovery Phase
A discovery phase is the part of the process that entails understanding the problem at hand by doing the appropriate research and analysis to guide further product development. In the product design cycle, three significant steps include:
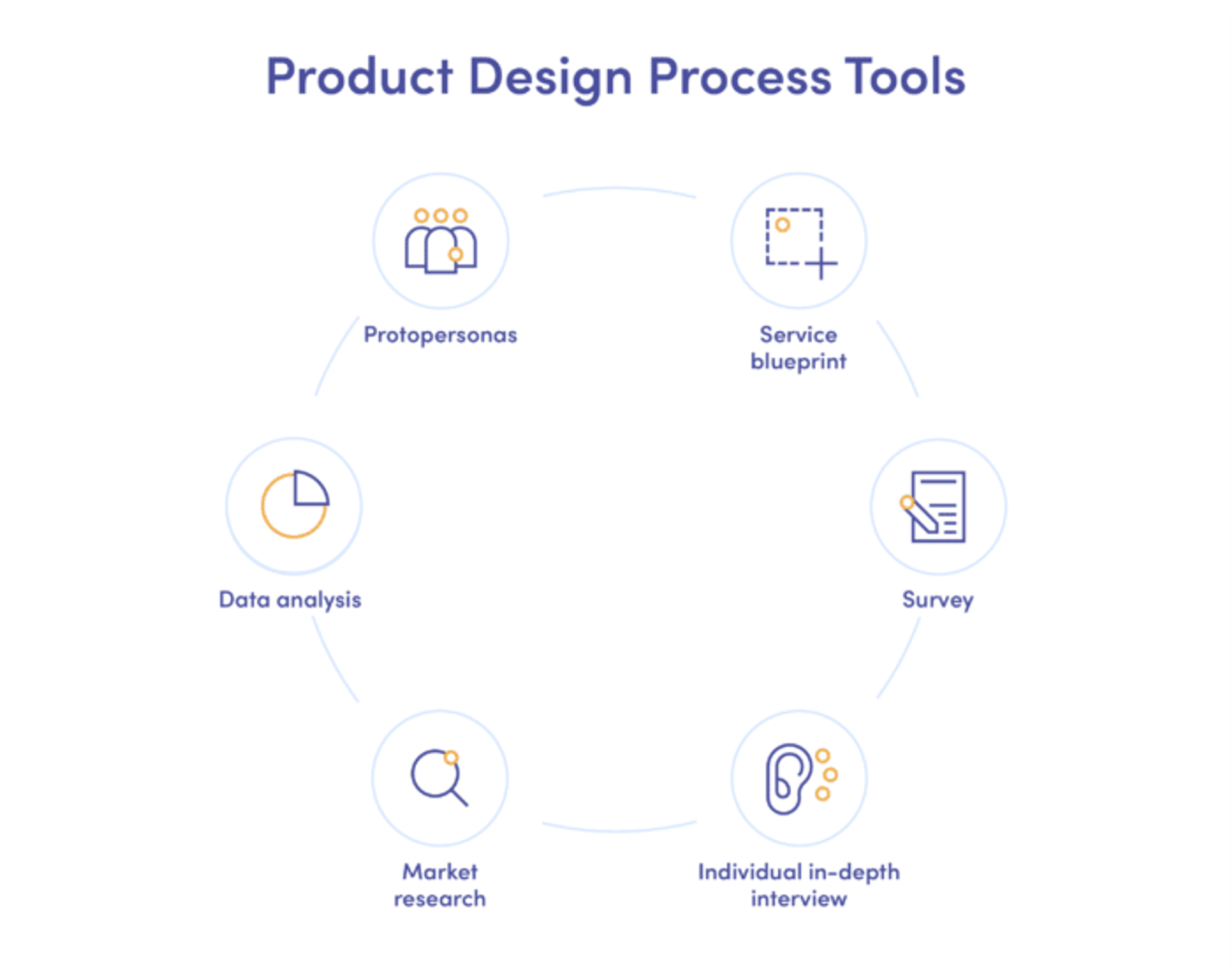
User Research Methods
To improve the design process, it is necessary to conduct user research to understand user preferences and behaviors and their pain points through various user research methods. These can include interviews, surveys, observations, and focus group discussions.
Market Analysis and Competitive Research
To gain a broader perspective on product design, it is useful to conduct user and market research to examine the market landscape and the products and strategies used by competitors. This assists in identifying areas where a product will be needed and how to position oneself in the marketplace where the product will be offered.
Identifying User Pain Points and Needs
This includes understanding the user's perspective and recognizing their pain points. This enables product designers to seek out real problems in the world and respond with appropriate solutions. It entails studying users' responses, testing the users in practical situations, and researching to understand the audience broadly.
Creating User Personas and Journey Maps
A persona portrays a potential market for specific user groups. It describes users' goals, characteristics, and reasons for using the application.
A journey map is a framework that outlines the user's experience and allows the designer to understand the user's interactions, pain points, and other points of contact during usage.
Source: careerfoundry

Stakeholder Interviews and Business Requirements
It is important to work with stakeholders such as business owners, product managers, and developers to design the product in line with business objectives and technical capabilities, emphasizing cross-functional collaboration. The requirement gathering and constraints understanding activities influence the design process.
During the discovery phase, the designers obtain a working knowledge of the three main components necessary for a successful product design: the user, the market, and the business. Working out these components assists the following stages of the product development process in designing innovative solutions relevant to the end user.
2. Definition & Strategy
The efforts made in the discovery phase are further developed and put into conclusion in the Definition & Strategy stage of the design process. Key activities occur during this phase, providing a clear direction and product development targets. Below are the main elements of product design workflow in the Definition & Strategy phase:
Problem Statement Formulation
It is essential to state that the product is supposed to address the aim. Formulating a comprehensive problem statement is intended to act as a guide for all design and development activities.
Setting Project Goals and Success Metrics
Establishing specific objectives and success metrics, guided by effective project management techniques, makes it clearer where the product will succeed. Such objectives and metrics will assist the firm in measuring the success of the products post-launch.
Defining Core Features and Requirements
It is also fundamental to identify the product's core features and requirements as determined in the discovery phase. This entails defining several functions, the core features required, and the expected level of such functionalities.
Prioritization Frameworks (MoSCoW, etc.)
The MoSCoW model is a good prioritization framework designed to measure the essentialness and need of specific features/requirements. This ensures that they start with the features that are most important first.
Source:medium

By carefully defining the problem, setting clear goals, and outlining essential features and requirements, the Definition & Strategy phase provides a solid foundation for the subsequent stages of product development.
3. Ideation & Conceptualization
In the Ideation & Conceptualization phase, there is action and creation as ideas are formed and then made into fundamental concepts. Various activities in this phase target idea creation, idea expansion, and concept development activities.
Utilizing modern prototyping tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of concept development. Activities in the Ideation & Conceptualization phase encompass:
- Brainstorming techniques: Engage in brainstorming sessions to encourage open and creative thinking, allowing team members to generate a wide range of ideas and concepts.
- Sketching of ideas and first concepts: Make rough sketches of ideas and come up with very preliminary concept designs to try to understand how the final solutions will look and also as a means of communication.
- Designing activities and interactive sessions: Engage members and other relevant participants by designing activities and interactive sessions. This will enable you to incorporate different and varied views to come up with effective ideas.
- Concept generation and concept selection: Prioritize and gauge the concepts generated using standards such as possible successful contributions to the project’s aim and intended objectives. Only the best and most realistic ideas should be chosen and worked on.
- Concept generation followed by concept testing: This activity starts by examining the different aspects of the project and later selecting the best strategies based on cost, practicality, or ability to use the resources.
The Ideation & Conceptualization phase occurs early in the product development process and narrows the focus to the ideas defining the final product.
4. Design & Prototyping
The Design and prototyping phase of the product development process is essential because it is the period within which ideas materialize into designs and stretches. This stage consists of several vital elements that realize the product’s image and set the stage for its manufacturing.
Information architecture: Establish an organization’s structure with explicit content and functional areas within the products and make it simple to navigate.
Source: linkedin

Wireframing and user flow: To demonstrate the overall arrangement and design of the main interaction areas, create a wireframe that outlines the user interfaces and maps out the user interface. Create user flows to detail the sequential order of events within the product.
Visual style: Create a look with colors, fonts, and images that convey the brand and customer expectations. Design systems should also be defined to encourage uniformity and expansion of all visual components of the product during its development.
Interactive Prototyping: This is the final phase, and it involves creating mockups, which are three-dimensional representations of the single-bil materials. The target audience should try to achieve these mockups in their products so that these prototypes will be very helpful.
Documentation and design specification: These could include decisions made by the design teams, the strategies and guidelines they provided, and the blueprint drafts created. Such documents ensure proper design implementation within the organization.
Several scholars view the design and prototyping phase as an essential stage in the growth of the product and its eventual execution. As thoughts become matter, the user interface is designed, and images are produced that reflect the general picture of the future prototype.
The phase paves the way for subsequent development and iteration, culminating in a successful product that meets user requirements.
5. Implementation & Launch
Once the design is completed in the implementation & launch phase, the life cycle of the product development is completed, meaning that an actual product is ready to be marketed. This phase stands along the following activities and concerns:
Developer Handoff
The designer works in tandem with developers so that there is a seamless transfer of design assets and specs. As such, adequate descriptive and prescriptive communication guarantees the construction of a design with minimal concerns.
Beta Testing and Usability Testing
The next stage of delivery of this new product is to introduce it to some people who can conduct beta tests. Based on feedback from beta testers, various suggestions on how to enhance the product, whether there are any issues people need to see, and how users interact with the product to improve user experiences are obtained.
Source:blog.hubspot

Quality Assurance
A systematic approach employs multiple testing stages to track down and address bugs, problems, and individual product inconsistencies. Quality assurance is a general term for ensuring that the intended product delivery has no flaws.
Launch Strategy
This stage strongly focuses on designing a launch strategy that will help many people. This includes designing promotional campaigns, public relations campaigns, and targeted audiences.
Post-launch Monitoring
The moment the product is launched, user feedback, metrics, and performance data can be constantly monitored and analyzed so that ongoing optimization and refinement can be done. Such a process is iterative, enabling the product to adapt to user demands and changing market environments.
Implementation & Launch is the phase where the product is formally introduced to the target consumers. It calls for teamwork, a very high concentration level, and ensuring end users have the best experience possible.
This is why a well-executed implementation and launch plan should be followed: the impact of the product on the market would be made, and competitiveness would be created for it.
6. Continuous Improvement
All these activities are under continuous improvement, which is most important in developing the product as it aims to improve it from the perspectives of the users, industry, and data.
It involves a cycle whereby the product or service is designed, developed, and subjected to evaluation and refinement to ensure it continues fulfilling its intended purpose. There are specific components within continuous improvement that we will outline below:
Analytics and Metrics Tracking
Using appropriate metrics makes it possible to engage in productive activities and understand users by providing and analyzing the necessary data. Such insights are valuable in making decisions and discerning the trends that require improvement.
User Feedback Loops
Different platforms, such as feedback forms, surveys, usability testing, customer support, etc., should be utilized to gather users’ thoughts on their pain points and suggestions on how to better address their concerns, ultimately enhancing the user's experience.
Performance Optimization
The smoothness of utilizing a product depends on how quickly the system works, how many errors occur, and how well it can scale with increased usage. Continuous improvements are thus imperative.
Source:jethrojeff

Regular Updates and Iterations
Whenever possible, user feedback and market demand should drive regular updates to existing products in the form of new features, fixes, enhancements, etc.
Product teams engaged in agile development should embrace the idea of improving the product consistently to retain and attract users and satisfy them with the product.
Common Pitfalls in the Product Design Process
Even well-intentioned product teams can stumble into traps that derail progress. Here are key challenges — and solutions — to navigate:
Scope Creep often arises when teams overload products with features, like a fitness app prioritizing meditation over core workout tracking. Counter this by using the MoSCoW framework to categorize features and setting clear, weekly-reviewed project goals.
Siloed Teams create misalignment, like developers receiving incomplete specs and building mismatched UIs. Foster collaboration via agile workflows, shared tools (Figma, Jira), and cross-functional workshops during prototyping.
Overlooking Technical Feasibility can trap startups, like planning AI features without data infrastructure. Involve engineers early and prototype high-risk elements with spike tests.
Neglecting Post-Launch Optimization leads to stagnation, like a productivity tool losing users to AI-driven competitors. Track KPIs, automate analytics, and schedule quarterly roadmap updates.
Key Considerations Throughout the Process
As long as one pursues continuous improvement in their processes or products, there are a few important things to remember. Such elements are essential in creating a unified product experience that is aesthetically pleasing and adheres to accepted norms within the industry. UX designers play a crucial role in ensuring that the product is user-friendly and meets the needs of the target audience.
- Design thinking principles: When someone adheres to design thinking principles such as empathy and the need for iteration, the concerns and pain points of the intended audience are addressed.
- Recording procedures: Effective recording details of what has already been created makes the work easy, as all information is preserved for future use and reference.
- Hardware and software: Proper hardware and software make product improvement less hectic by facilitating communication, design, testing, and deployment.
Lastly, as long as all these factors are observed by the team when improving the product(s), their product(s) will stand the test of time and competition and be cherished by the consumers; hence, customer satisfaction is guaranteed.
Read more:
Conclusion
To conclude, it can be argued that continuous product upgrades and tweaking are critical as they provide a competitive advantage while satisfying users' needs. Product teams undertake initiatives such as collecting user feedback, improving efficiency, and maintaining design systems, and since the focus is on the product's value, it should be useful for users.
Throughout the cases, other issues, including functional collaboration, design thinking and processes, proper documentation, and relevant tools and software, enhance the chances of success in carrying out product development activities.
Regular interaction with stakeholders in the project's management circle mitigates the risk of disorientation due to changes within organizations in certain areas. This ensures that business improvements also relate to the organization's objectives.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


